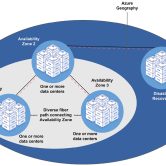
Azure regions are geographic locations around the world where Microsoft has established data centers. Each region contains multiple data centers that are logically grouped together to provide redundancy and high availability. These regions are interconnected through a dedicated low-latency network, ensuring seamless connectivity and data transfer. As shown in the following figure, there are different Regions with Availability Zones and Datacenters.
Praesent laoreet convallis tellus. Donec nulla orci, rutrum sit amet nisi at, pharetra auctor justo. Pellentesque et malesuada odio. Curabitur lectus erat, malesuada non dolor vel, pellentesque scelerisque nunc. Morbi non aliquam sapien, id gravida tellus. Sed eleifend vulputate volutpat. Duis id erat nec ipsum elementum luctus nec vel nibh.

Why Regions Matter
Donec ut consectetur augue, at gravida orci. Donec nec est quis massa suscipit faucibus vitae id tellus. Vestibulum et leo sem. Aliquam viverra arcu mattis orci vestibulum tristique. Sed in gravida arcu.
1. Latency and Performance:
By selecting a region close to your end-users, you can minimize latency and improve application performance. For example, if your primary user base is in Europe, deploying your application in an Azure region in Europe will provide faster response times compared to a region in North America.
2. Compliance and Data Sovereignty:
Different regions may have specific regulatory and compliance requirements. Choosing a region that complies with local laws and regulations is essential for meeting data sovereignty requirements. For instance, a financial services company operating in Germany might choose the Germany West Central region to ensure compliance with local data protection laws.
3. Redundancy and Disaster Recovery:
Availability zones are ideal for setting up disaster recovery solutions. You can replicate data and services across zones to ensure quick recovery in the event of a failure. For example, an e-commerce website can deploy its web servers in one zone and its database servers in another, ensuring that both tiers remain operational during an outage.
We will jump into real world scenarios where we will learn how to put together these services from design to implementation to achieve most of the needs within your organization.
CssLabs- saroj
Examples of Services Supporting Availability Zones
- VMs: Deploy VMs across zones to ensure high availability.
- Managed Disks: These store VM disks in different zones to prevent data loss.
- Load Balancers: These distribute traffic across zones for balanced and resilient application delivery.
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): These deploy AKS nodes across zones for resilient container orchestration.
- SQL Databases: These use zone-redundant databases to protect against zone failures.
Designing for High Availability and Resilience
To design high-availability applications on Azure, it’s essential to leverage both regions and availability zones effectively. Here are some strategies:
- Multi-Region Deployment: This ensures application availability by deploying across multiple regions.
- Zone-Redundant Architecture: This increases fault tolerance by distributing components across availability zones.
- Automated Failover and Recovery: This minimizes downtime with automated failover mechanisms.
- Regular Testing and Monitoring: This ensures readiness with regular disaster recovery testing and monitoring.